辅助指令
help工具
help 目录名 显示指定目录中的所有命令及其函数
help lang 将列出与 MATLAB 编程语言的所有命令及其函数
help matfun 将列出与数值线性代数有关的所有矩阵函数
help elfun 列出所有基本函数
- help 命令名/函数名/符号 显示指定的命令名/函数名/符号的详细信息
例:显示计算矩阵特征值和特征向量的函数eig的说明
1 | help eig |
lookfor工具
首先可以使用上面学到的help工具了解lookfor的功能:
lookfor Search all M-files for keyword.
lookfor XYZ looks for the string XYZ in the first comment line
(the H1 line) of the HELP text in all M-files found on MATLABPATH
(including private directories). For all files in which a
match occurs, lookfor displays the H1 line.
For example, “lookfor inverse” finds at least a dozen matches,
including the H1 lines containing “inverse hyperbolic cosine”
“two-dimensional inverse FFT”, and “pseudoinverse”.
Contrast this with “which inverse” or “what inverse”, which run
more quickly, but which probably fail to find anything because
MATLAB does not ordinarily have a function “inverse”.
lookfor XYZ -all searches the entire first comment block of
each M-file.
In summary, WHAT lists the functions in a given directory,
WHICH finds the directory containing a given function or file, and lookfor finds all functions in all directories that might have something to do with a given key word.
lookfor指令机制:
对MATLAB中的每个 M 文件注释区的第一行进行扫描,一旦发现包含要查询的字符串就显示出来提示用户。也可利用此机理建立自己文件的在线帮助。
其他帮助指令
exist 检查指定名字的变量或函数文件的存在性
what 按扩展名分类列出 在搜索路径中 指定目录上的文件名
which 列出指定名字文件所在的目录
数值计算
数值矩阵
- 利用指令
reshape创建数值矩阵
1 | av=1:15 % 产生15个元素的行向量 av 以% 开头的是注释行 |
1 | >> av=1:15 |
- 利用指令
diag产生对角阵
1 | ar=rand(4,4) % 产生 4x4 的 0-1 均匀分布随即矩阵 ar |
1 | >> ar=rand(4,4) |
矩阵标识
1 | >> b=[1 2 3 4 5; 6 7 8 9 10 ;11 12 13 14 15] |
- b23=b(2,3)
b23代表矩阵b中第二行第三列的数值
- b1=b(1:2,[1 3 5])
将变量b1赋值为矩阵b中第一行、第二行中的1、3、5列数值
- b2=b([3 1],:)
将b2矩阵赋值为第三行、第一行的所有列数值
- b([1 3],[2 4])=zeros(2)
将原来b矩阵中的一三行的二四列赋值为0
条件选择
1 | x=[1 2 3 4 5] %产生 1x5 向量 |
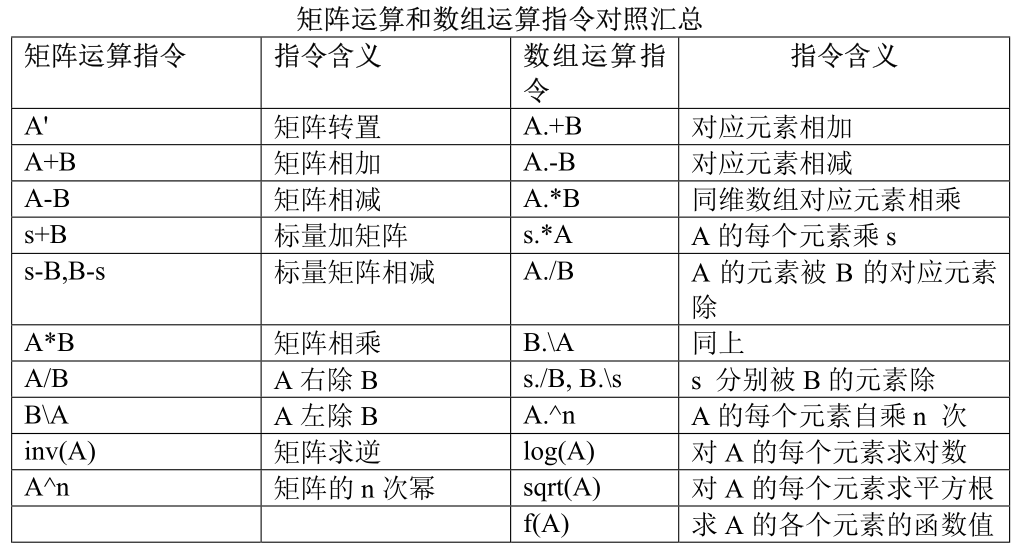
数组运算
1 | >> a=[1 2 3; 4 5 6; 7 8 9]; |
